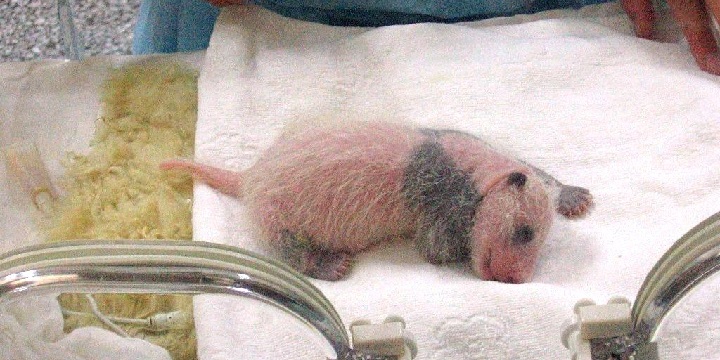
Giant panda became icon species for ex-situ conservation, and for nature conservation efforts in general. Natural habitat of the wild individuals lies in central China in Sichuan province. The biggest threats to Giant panda are habitat loss and fragmentation. Since long time great effort was dedicated to saving this species. Part of the conservation effort was establishing many of the captive breeding centers. But facing of the mentioned challenges, the program was complete failure for a long time.
The main challenges include difficulty of mating, resulting in low pregnancy rate; high mortality of offspring; natural behaviors loss, and familiarizing with the human.
After extensive research all the problems were solved. For example, artificial insemination was performed successfully.
Copulation and birthrate can be also greatly improved if pandas can freely choose mating partner. It was discovered that high mortality rate of young is attributed to constipation, and solution to this problem was performing massage to help with the bowel movement. Giant pandas often give birth to twins, and in nature panda mother only focus on the stronger twin resulting in the death of another one. This was solved by swapping the twins and letting mother care for only one offspring at the time, while the other one was under the care of husbandry workers.